Leaf-spot disease of Brassica
Blight of Crucifers
Host: Brassica spp. (Mustard, Cabbage, Radish, Sarson, Rai, etc.)
Pathogen: Alternaria brassicae
Pathogen: Alternaria brassicae
Distribution
It is one of the common diseases of crop plants in northern India, which decreases the yield significantly. The disease is caused by Alternaria brassicae.
Symptoms
 |
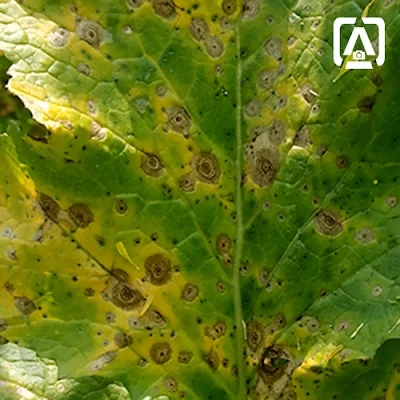 |
| Mustard leaf showing spots |
Leaf spot showing concentric rings |
The leaf of the infected plant shows round to irregular concentric spots. In severe cases, the symptoms may be seen on leaves, stem and even on pods of sarson (Brassica campestris L.).
Pathogen
Alternaria brassicae (Berk.) Sacc. is the causative fungus of this disease. Fungus grows inter or intracellularly in the host. Conidiophores arise from the mycelium after a few days of limited growth. One to several conidia may develop (singly or in chain) at the tip of conidiophores. The conidia are bottle-like with a long beak and narrow base. The body of the conidia are septate with several cross and vertical septa (see photograph) and also called muriform conidia.
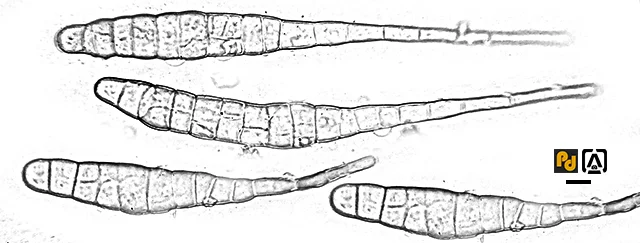 |
| Conidia of Alternaria brassicae. bar = 20 μm |
Nature and recurrence of the disease
The disease is soil born and seed-born. Conidia of the pathogen survive in the soil and in the debris. On getting host in moist weather they germinate and cause primary infection. In foggy weather with high relative humidity conidia germinate and cause secondary infection.
Control measures
- Crop rotation with non-crucifer plants, seed treatment, sanitation and use of resistant varieties are useful control measures.
- Deep ploughing in summer reduces the disease incidence.
- Early-sown mustard is free from this disease. In the Indian sub-continent, mustard sown before October is free from diseases.
- Seed should be treated in hot water at 50 °C for 20 minute.
- In order to prevent the crop from leaf spot, fungicide (Copper oxychloride or Mancozeb or Zineb @ 2.5 g/l) should be sprayed at 15 days intervals from 6 week after sowing.
- Use blight-resistance varieties of mustard.
- Recently Anand et al. (2023) tested the efficacy of aqueous garlic bulb extract against Alternaria brassicae under laboratory conditions and reported 100% inhibition in conidial germination.
References
- Anand M., Akhtar O., Shahbaan M., Zoomi I., Pandey D. "Evaluation of antifungal activities of some plant extracts against Alternaria brassicae causing spot disease of mustard" . International Journal of Botany Studies, Volume 8, Issue 12, 2023, Pages 24-31
White
rust disease of Mustard
Blister disease of Crucifers
Host: Brassica campestris (L.)
Pathogen: Albugo canida (syn. Cystopus candidus)
Pathogen: Albugo canida (syn. Cystopus candidus)
Distribution
The disease is of global distribution and reported from more than 50 countries. White rust disease of Crucifers
causes up to 90 % loss in annual yield (Saharan et al. 2014). The disease reduces the total yield as well as quality of nutrients in the mustard crop.
Symptoms
 |
| Underside of the mustard leaf showing white pustules (blisters) |
Early symptoms appear in the form of white raised pustules only at the lower side of the leaves. At maturity,
these blisters get ruptured and powdery mass of conidia come out in forms of white rust. In severe infection, pathogen attacks the floral parts and induces hyperplasia
and hypertrophy in the floral part. The infected inflorescences are malformed and fruits
become abnormal.
Pathogen
 |
| Albugo conidia with conidiophore |
The disease is caused by oomycetous fungus, Albugo candida (syn. Cystopus candidus). It is an obligate parasite (biotroph). Pathogen produces a basipetal chain of sporangia/conidia born on the small club-shape conidiophores inside the pustules. The nature of sporangia or conidia depends upon the temperature and humidity. If adequate moisture is available, it germinates into six zoospores and behaves like a sporangium, whereas in low moisture conditions, it germinates directly by producing germ tubes and behaves as a conidium. The zoospores are naked (lacking cell wall), reniform (kidney-shaped) and bi-flagellate. The flagella are inserted laterally. Towards the end of the host season, fungus becomes systemic and develops oospores in the infected parts. These oospores are thick walled resistant structures and help in perennation of disease.
Control measures
- According to Saharan et al. (2014), no single method is effective in managing the white rust of crucifers. Therefore, adapting more than one control measures like, cultural, chemical, biological and host resistance are suggested.
References
- Saharan, G.S., Verma, P.R., Meena, P.D. and Kumar, A., 2014. White rust of crucifers: biology, ecology and management. Springer.
Content first created on 14-11-2020
last updated on 15-12-2023
last updated on 15-12-2023

